- Home
- Livestock
- Animal and Plant Health Laboratories
- EU Reference Laboratory
- Bluetongue disease
Transmission and pathogenesis
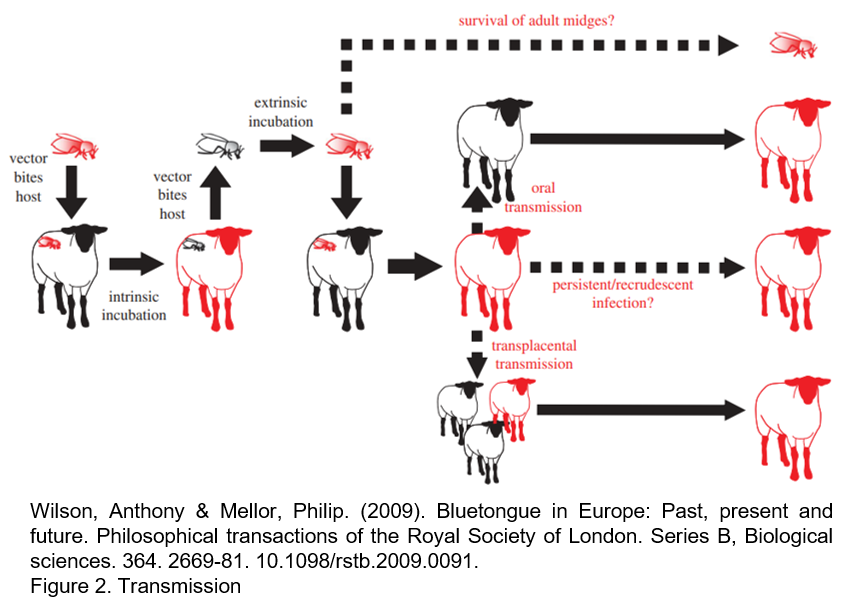
BTV is an arbovirus that is transmitted between its mammalian hosts by competent species of Culicoides biting midges. BTV transmission can also occur through the semen of infected animals, and specific strains/serotypes have been shown to cross the placental barrier. Both ways of transmission have been confirmed in the wild-type BTV-8 strain which affected northern Europe since 2006. Current literature indicates that vector-free horizontal transmission of BTV probably is an infrequent event which requires close contact of animals. The relevance for the epizootiology is therefore limited.
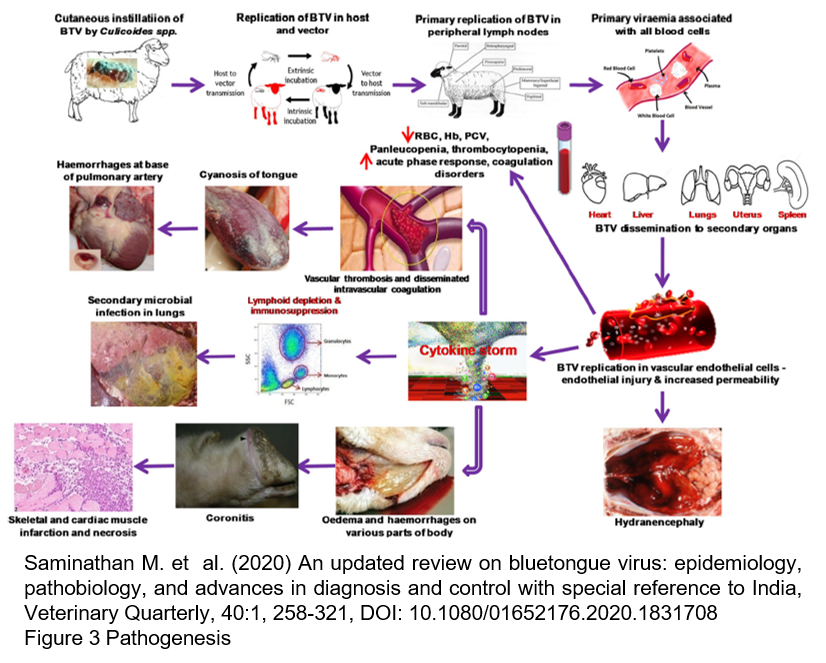
After an initial replication in agranular leucocytes at the site of inoculation and in regional lymph nodes, infected lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells, and macrophages disseminate the virus to secondary sites (mainly lungs, spleen, and lymph nodes). Infectious BTV can be detected associated with erythrocytes, in which it does not replicate but persists in invaginations of cell membranes. Association of infectious BTV with erythrocytes is detected soon after infection (24 h) and persists throughout the duration of viraemia, protecting the virus from immune clearance. In ruminants a prolonged cell-associated viraemia persists even in the presence of high levels of neutralizing antibodies. Infectious virus had been isolated from blood samples collected until 60 days postinfection in cattles. According to species, age, and serotype, BTV RNA can be detected by RT-PCR long after.
BTV infection in ruminants induce rapid antibodies production to both structural and nonstructural proteins. Neutralizing antibodies confer a long-lasting protection to reinfection by a homologous BTV serotype. The level of neutralizing antibodies detected by serum neutralization tests (SNT) does not necessarily correlate with the degree of protection. Cellular immunity plays an important role in protection against BTV infection. Antibodies to VP7 are group-specific, VP7 being well conserved between different serotypes. Detection of anti-VP7 antibodies is currently used for serological diagnosis of BTV infection using several ELISA tests.